Laboratory of GlycoChemistry (№ 23)

ORCID ID: 0000-0003-1858-7738
Researcher ID: B-1004-2008
h-index: 30 (Google Scholar), 26 (Scopus), 24 (Web of Science)
- Development of methodologies for the chemical synthesis of biologically significant carbohydrates—including monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides—and diverse glycoconjugates derived therefrom.
- Synthesis of carbohydrate antigens for the diagnosis of socially significant diseases and diseases posing a danger to others (including the diagnosis of mycobacteriosis).
- Study of the structure of reaction solutions in order to optimize chemical reactions.
- Flow chemistry.
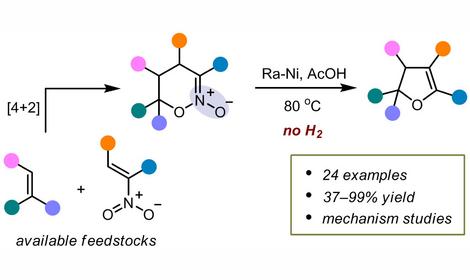
✓ Deacetylation of O-acetylated pyranose glyco-oxazoline obtained from N-acetyl-D-glucosamine using sodium methoxide in methanol selectively affords the expected pyranose triol at room temperature. In contrast, heating (60 °C) results in the formation of a previously unknown, thermodynamically favorable furanose isomer of the glyco-oxazoline triol. Isomeric O-acetylated pyranose glyco-oxazolines obtained from N-acetyl-D-galactosamine or N-acetyl-D-mannosamine also afford furanose isomers of the corresponding glyco-oxazoline triols when treated with MeONa in MeOH at 60 °C. A mechanism for this rearrangement was proposed and validated by DFT calculations at the r2SCAN-3c/CPCM (MeOH) level of theory. The obtained results open a new route to poorly studied furanose forms of glyco-oxazolines containing various O-protecting groups. [DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2025.109761]
✓ Over the past decades, the 4-methoxyphenyl group has been widely used to protect the anomeric center during the block syntheses of various complex glycans due to its ease of introduction and removal, stability under various conditions, and orthogonality with many other commonly used protecting groups. However, despite all the advantages of glycan glycosides with a 4-methoxyphenyl aglycone, efficient and stereoselective introduction of functional groups into the aglycone of such glycans can be difficult, limiting the preparation of glycoconjugates based on them. Conditions for the functionalization of 4-methoxyphenyl aglycone have been identified, which, under optimized conditions, proceeds in high preparative yields. The key step is the selective removal of the methyl group from the 4-methoxyphenyl aglycone. Subsequent substitution of the phenolic hydroxy group in the resulting 4-hydroxyphenyl glycosides with various alkylating agents effectively leads to the formation of target glycosides with diverse functional groups in the aglycone. The developed synthetic approach allows the preparation of derivatives with functional groups in the aglycone at any stage of oligosaccharide synthesis from a single precursor with 4-methoxyphenyl aglycone. The obtained results indicate that 4-methoxyphenyl aglycone can be considered as a cleavable pre-spacer aglycone (Janus aglycone). [DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2025.109544]
✓ A comparative study of 13 sialyl halides evaluated their reactivity and stereoselectivity in glycosylations with methanol and isopropyl alcohol. It was established that the nature of the leaving and protecting groups, along with the nucleophilicity of the alcohol, critically determines the reactivity of the sialyl halides and the reaction route, which in turn affects stereoselectivity. Electron-withdrawing groups destabilize the glycosyl cation and enhance α-stereoselectivity, directing the reaction along an associative SN2-like pathway. Reducing the nucleophilicity of the alcohol or increasing the nucleofugality of the leaving group increases the contribution of the dissociative SN1-like route, allowing nucleophilic participation of remote groups that can either increase (AcNH/TFANH–C(5) participation) or decrease (AcO–C(4)/C(7) participation) the share of the α-glycoside. These results open new avenues of research for the development of more efficient and selective sialyl donors. [DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.4c02759, 10.1016/j.carres.2025.109617]
✓ A new strategy for synthesizing fragments of cell wall polysaccharides from the tuberculosis pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis has been developed. This strategy utilizes the silylated Ara-β-(1→2)-Ara diarabinofuranoside, which significantly reduces the number of steps. Using this methodology, a branched hexaarabinofuranoside containing a 4-(2-chloroethoxy)phenyl aglycone was obtained, which was successfully converted into a glycosyl donor. This enabled the synthesis of a branched decaarabinofuranoside containing a 4-(2-azidoethoxy)phenyl aglycone spacer. The synthesized oligosaccharides and neoglycoconjugates derived from them expand the library of oligoarabinofuranoside-based antigens related to fragments of mycobacterial cell wall glycopolymers. Such libraries hold promise for the development of new multi-epitope tests for the serological diagnosis of tuberculosis and leprosy. [DOI: 10.3390/molecules30153295]
✓ A protected glycoside donor based on Ara-β-(1→2)-Ara diarabinofuranoside, containing exclusively tert-butyldiphenylsilyl groups, was synthesized from the corresponding 4-(2-azidoethoxy)phenylglycoside. The resulting diarabinofuranoside was successfully used to prepare branched β-(1→2), α-(1→3)-, α-(1→5)-dodecaarabinofuranoside. This oligoarabinofuranoside can be considered a promising mimetic of mycobacterial cell wall glycopolymer fragments, which can find application in the development of new multiepitope tests for the serological diagnosis of tuberculosis. [DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2025.109622]
✓ An unusual oligomerization reaction of arabinofuranosides has been discovered, occurring in the presence of trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. A study of the mechanism of this transformation revealed that the nature of the acid catalyst used significantly affects the process outcome. The octa-, dodeca-, and hexadecaarabinofuranosides obtained by this method can serve as useful building blocks in the synthesis of oligosaccharide fragments of Mycobacterium tuberculosis polysaccharides. [DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2024.109141]
✓ A mild and general protocol for the chemoselective deacetylation of mixed acetyl- and benzoyl-protected carbohydrates under mild acidic conditions has been developed. The protocol provides rapid access to partially protected carbohydrate derivatives that serve as versatile synthetic building blocks in the total synthesis of various mono- and oligosaccharides. The applicability of the developed protocol has been successfully demonstrated on a number of differently substituted carbohydrate substrates with various configurations and bearing functionalized aliphatic and aromatic aglycones. The protocol has shown excellent compatibility with widely used O-anomeric protecting groups, pre-spacer aglycones, and thioglycoside glycosyl donors. [DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.4c00900]
✓ The development of new methods for chemical glycosylation typically involves comparing different glycosyl donors. An attempt to compare the chemical properties of two sialic acid-based thioglycoside glycosyl donors, differing only in the substituent at O-9 (trifluoroacetyl or chloroacetyl), at different concentrations (0.05 and 0.15 mol/L) led to mutually exclusive conclusions regarding their relative reactivity and selectivity, which prevented us from identifying the possible influence of the remote protecting groups at O-9 on the glycosylation outcome. Judging by the results of supramer analysis of reaction solutions, this problem may be related to the formation of supramers of glycosyl donors that differ in structure and, consequently, in chemical properties. These results apparently indicate that comparing the chemical properties of different glycosyl donors may not be as simple and unambiguous as is commonly believed. [DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.20.18]
✓ Glycosyl halides were historically among the first glycosyl donors used in glycosylation reactions, and there is currently growing interest in glycosylation reactions involving this class of glycoside donors. New methods for their activation have been proposed, and efficient syntheses of oligosaccharides with their participation have been developed. However, the possibilities of using these approaches to the synthesis of sialosides are limited by the small variety of known sialyl halides (previously, sialyl chlorides were primarily used, less commonly sialyl bromides and sialyl fluorides, with acetyl (Ac) groups at the oxygen atom and AcNH, Ac2N, and N3 groups at C-5). This work describes the synthesis of six new N-acetyl- and N-trifluoroacetylsialyl chlorides and bromides with O-chloroacetyl and O-trifluoroacetyl protecting groups. The preparation of N,O-trifluoroacetyl-protected derivatives became possible due to the development of a synthesis of sialic acid methyl ester pentaol with N-trifluoroacetyl group. [DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2024.109033]
✓ Flow chemistry offers a number of advantages for conducting chemical reactions and has become an important area of research. It might seem that sufficient knowledge has been accumulated on this topic to understand how to select a microreactor/micromixer design and flow rate to achieve the desired reaction outcome. However, some experimental data are difficult to explain based on generally accepted concepts of chemical reactivity and the characteristics of microfluidic systems. This mini-review attempts to identify such data and offer a rational explanation for unusual results based on a supramer approach. It is shown that varying the flow regime (determined by mixer design and flow rate) can either improve or worsen reactivity and lead to completely different products, including stereoisomers. Mixing the reactants at maximum efficiency is not necessary. The real problem is in proper mixing of the reactants, since at too high or too low a flow rate (in a given mixer) the reactant molecules are incorrectly presented on the surface of the supramers, which leads to a change in the stereoselectivity of the reaction, or they form tight supramers in which most of the molecules are located inside the core of the supramers and are not accessible for attack, which leads to low yields. [DOI: 10.3390/inventions8050128]
✓ Phase-transfer catalysis (PTC) is widely used in glycochemistry to obtain aryl glycosides via glycosylation. While investigating the possibility of synthesizing 4-(3-chloropropoxy)phenyl sialoside (Neu5Ac-OCPP) from N-acetylsialyl chloride with O-acetyl groups (1), we have recently discovered a strong dependence of the glycosylation result under PTC conditions on the reagent mixing mode: in a flask, only the α-anomer of Neu5Ac-OCPP was obtained, albeit in low yield (13%), whereas under microfluidic conditions, the yield of Neu5Ac-OCPP increased to 36%, although stereoselectivity decreased (α/β ≤ 6.2). In this work, it was found that the result of this reaction, carried out under microfluidic conditions using a Comet X-01 micromixer (at a flow rate of 2 μL/min), nonlinearly depends on the concentration of N-acetylsialyl chloride 1 (5–200 mmol/L). The target Neu5Ac-OCPP was obtained in a significantly higher yield (up to 66%), accompanied by increased stereoselectivity (α/β = 17:1 – 32:1) at high concentrations (C > 50 mmol/L), whereas the yield (10–36%) and especially the stereoselectivity (α/β = 0.9:1–6.2:1) were noticeably lower at low concentrations (C ≤ 50 mmol/L). Such a sharp, abrupt increase in stereoselectivity above the critical concentration (50 mmol/L) is apparently associated with a change in the presentation of molecules on the surface of the glycoside donor supramers existing in different concentration ranges. [DOI: 10.3390/catal13020313]