Laboratory of Carbenes and Other Unstable Molecules (№1)

ORCID: 0000-0002-3161-3585
Researcher ID: L-6095-2013
h-index = 23 (WoS)
- Investigation of labile intermediates of chemical reactions by matrix IR spectroscopy;
- Reactivity and physico-chemical properties of labile and stable organic and organoelement ion radicals;
- Organic and organoelement synthesis and electron-induced synthesis;
- Study of electrocatalytic multicomponent and cascade processes for the selective production of pharmacologically active heterocyclic systems;
- Development of classical catalytic, as well as "solvent-free" and "on-solvent" multi-component processes for the selective production of pharmacologically active heterocyclic systems.
✓ The formation of complex Cl2Si→CO has been recorded by IR spectroscopy in argon matrices. The positive shift of the n(CO) band and the theoretical structure analysis indicate the complex to be non-classical carbonyl one. This is the first experimentally registered non-classical silylene carbonyl complex. The main photo-transformation direction is a decomposition into initial reagents. The potential energy surface of the SiCl2+CO system has been theoretically studied. It is shown that further thermal transformations of the complex are not energetically advantageous.
✓ The interaction of SiCl2 with 1,3-butadiene has been studied by matrix IR spectroscopy. It was found that the reaction can stop at the formation of 1:1 complex under low-temperature (10 K) in inert (Ar) matrices. Using this reaction system, the photochemical interaction of silylenes with conjugated dienes has been performed for the first time. It has been shown that the photo-induced complex transformation leads to 1,1-dichloro-1-silacyclopent-3-ene and labile 1,1-dichloro-2-vinyl-1-silacyclopropane in comparable amounts. In contrast to photo-induced complex transformation, the thermal interaction of SiCl2 with 1,3-butadiene produces 1,1-dichloro-1-silacyclopent-3-ene only. So, 1,1-dichloro-2-vinyl-1-silacyclopropane is kinetically and thermodynamically less advantageous under high temperature.
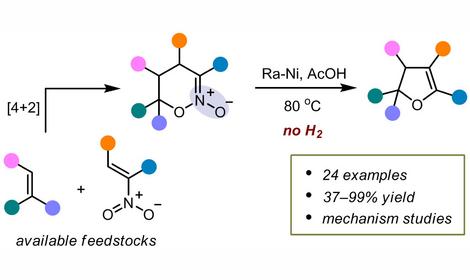
✓ An effective multicomponent transformation of salicylic aldehydes, 2-aminoprop-1-ene-1,2,3-tricarbonitrile and 4-hydroxypyridine-2(1H)-ones, into previously unknown 5-(4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-yl)-5H-chromeno[2,3-b]pyridines has been developed (yield of 70-97%). New solvent-catalyst system has been used. The heterocyclic systems obtained belong to compounds known as ‘privileged medicinal scaffolds’, which actively interact with biological receptors and are characterized by pronounced biochemical and pharmacological activity.
✓ An effective morpholine-catalyzed multicomponent transformation of salicylic aldehydes, 2-aminopropyl-1-ene-1,2,3-tricarbonitrile and trialkylphosphites into previously unknown 5-dialkylphosphonate-substituted 2,4-diamino-5H-chromene[2,3-b]pyridines (yield of 56-86%) has been developed. The heterocyclic systems obtained belong to compounds known as ‘privileged medicinal scaffolds’, which actively interact with biological receptors and are characterized by pronounced biochemical and pharmacological activity.
✓ An electrosynthesis of copper nanoparticles using methyl viologen (redox mediator) and a soluble Cu anode (a source of copper ions) has been developed. The process is well controlled by the change in the solution color. The particles were identified using CV, electron microscopy, and X-ray diffraction analysis.
✓ A number of approaches to anodic C-H thiocyanation of (het)arenes having various structures and reactivity (anilines, dihydroxybenzenes, pyrroles, indoles, pyrazole[1,5-a]pyrimidines, azopyrazoles) is proposed. As a result, over 20 original mono-, dithiocyanato-, and azolylthiocyanato-substituted (get)arenes have been synthesized with a yield of up to 90%. The revealed antifungal activity of the obtained substances is comparable or superior to modern antifungal drugs (fluconazole, itraconazole, amphotericin B), which ensures the applied development of these studies.
✓ The mechanism of electrochemical reduction of potentially biologically active benzo(a)phenazine-7,12-dioxide and acenaphtho-1,4-quinoxaline dioxide in DMF (0.1M Bu4NClO4) has been studied by cyclic voltammetry, chronoammetry, and electrolysis at a controlled potential. It has been shown that these compounds, during one-electron reduction, form sufficiently stable radical anions in a non-aqueous medium. In the presence of proton donors, the compounds decompose with the cleavage of the ·OH radical. According to the literature, the formation of the ·OH radical as a result of the bio-reduction of dioxides determines their activity as biological agents.
✓ Together with the I. Alabugin’s laboratory (University of Florida, USA), the concept of electron upconversion was proposed, developed and described. Two general types of systems are presented – dissociative (functioning on the basis of intramolecular fragmentation) and associative (based on the bimolecular formation of a three-electron bond). It has been shown that possible applications of reducing agent upconversion include electrocatalytic processes, photoredox cascades, drug design, DNA photoreparation, etc.
✓ A new environmentally friendly approach to the electrodeposition of germanium nanoparticles for use in high-capacity lithium-ion batteries has been proposed. The method avoids the use of aggressive, toxic, and chemically unstable germanium halides by replacing them with germanium citrate. The citric and acetic acids used in this process, propylene glycol (as well as water) belong to the food category, and the toxic effects of germanium citrate are comparable to those of sodium chloride. Based on the materials obtained, lithium-ion batteries are designed that are not inferior in their characteristics to samples manufactured using traditional environmentally unsafe technology. New, simple and effective approaches to the formation of practically useful silicon and germanium-containing products have been developed. Nanoparticles which have shown excellent results as anodes for lithium–ion batteries have been obtained based on water-soluble 2-carboxyethylsesquioxide. They are stable during multiple cycling and have a capacity up to two times higher than the maximum available for graphite currently in common use. A method for obtaining fluorescing nanoporous silicon based on electrochemical etching using ionic liquids instead of hydrofluoric acid, which is currently traditionally used for this purpose, is proposed.
✓ Based on a comprehensive study of multicomponent reactions involving carbonyl compounds and C-H acids, a simple and effective synthesis of spirocyclopropane barbiturates has been developed (yield of 75-90%). The method involves the interaction of aldehydes, N',N'-dimethylbarbituric acid and malonitrile. Spirocyclopropylbarbiturates are a class of compounds with pronounced pharmacological activity used in the treatment of arthritis and as antitumor agents. Molecular docking has shown that the obtained structures are potentially promising compounds in pharmacology.
✓ A multicomponent tandem Knevenagel-Michael reaction was discovered. Reaction of benzaldehydes, N,N'-dimethylbarbituric acid and 4-hydroxy-6-methyl-2H-piran-2- in alcohol media at ambient temperature leads to substituted asymmetric spiro[furo[3,2-c]piran-2,5'-pyrimidine]s having two different heterocyclic rings. This process is a very convenient way to obtain substituted spiro[furo[3,2-c]pyran-2,5'—pyrimidines], useful compounds for various pharmacologically active compounds. The mild and simple conditions of this chemical multicomponent process, as well as the non-chromatographic isolation procedure, lead to excellent yields of the target substances. Thus, this new multicomponent strategy using the Knevenagel-Michael tandem reaction and further oxidative cyclization is a selective and effective way to obtain asymmetric spiro[fourier[3,2-c]pyran-2,5'-pyrimidines].
✓ The data on the oxidative addition of tetrylenes to various substrates containing a single bond are systematized. The causes influencing the direction and rate of oxidative addition reactions have been identified. It has been shown that the reactivity of C-substituted tetrylenes significantly depends on the values of the valence angle and the HOMO-LUMO gap, and intramolecular donor-acceptor interactions between the tetrel atom and donor molecules or functional groups of the ligand can also change the direction of oxidative addition reactions. In the case of O-substituted tetrylenes, the monomeric or oligomeric state is the main factor influencing the reactions of oxidative addition. Tetrylenes based on redox-active catecholate or o-amidophenolate ligands undergo oxidation of the redox-active ligand in the presence of halogens or compounds with weak O-single bonds. Doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2025.216469
✓ New mono- and binuclear Sn(IV) complexes have been synthesized and characterized. Cyclic voltammetry was used to estimate the HOMO-LUMO gap. It is shown that the introduction of Sn(IV) into the Schiff bases makes it possible to significantly narrow this gap. Doi: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2025.123527.
✓ A series of plumbylenes containing redox-active ligands has been synthesized. The thermal analysis of the obtained compounds and the initial ligands was carried out. It has been shown that the complexation with lead leads to a significant narrowing of the HOMO-LUMO gap. Also, complexation with lead leads to quenching of the fluorescence of the organic ligand. It has been established that the product of electrochemical reduction of plumbylenes is metallic lead. Doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2025.122724.