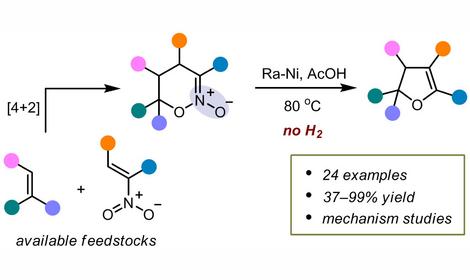
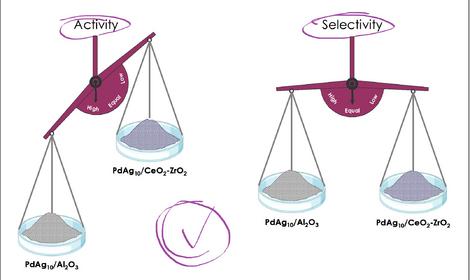
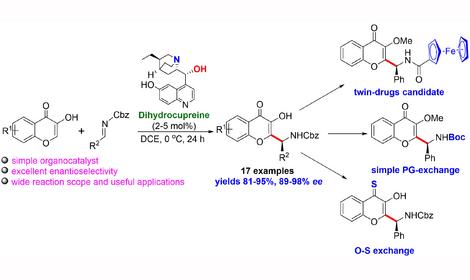
Laboratory of Catalytic Reactions of Carbon Oxides (No 40)

ORCID: 0000-0002-1052-9237
Researcher ID: G-9585-2017
h-index: 16 (Scopus), 18 (РИНЦ)
- Synthesis of hydrocarbons from CO and H2 (Fischer–Tropsch synthesis) and related reactions
- Catalytic carbonylation of organic compounds
- Kinetics and mechanisms of lower alkanes transformations on heterogeneous catalysts: dehydrogenation, isomerization, and aromatization reactions
✓ RuCo catalysts prepared by modifying the support with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, urea, acetone azine, or citric acid was investigated for the first time in order to see the effect of the ligand on the catalytic properties of the bimetallic system. The catalysts were characterized by TEM, STEM, XRF, H2-TPR, NH3-TPD, and XPS. It was assumed that total acidity, reducibility, dispersion and atomic surface composition of the catalysts are dependent on the ligands used. It has been shown that catalytic properties (activity, selectivity for higher hydrocarbons, chain growth factor) can be optimized by selecting an appropriate ligand surface modifier. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.150837
✓ Efficient synthesis of 2-arylpropanoic acids by Pd-catalyzed carbonylation of vinyl arenes with CO and HCOOH is reported. Excellent regioselectivity to target 2-arylpropanoic acids is achieved by the addition of some polyvinylpyrrolidone. Mild reaction conditions and available catalytic system and low Pd loading are the advantages of the proposed protocol. It was used in the total synthesis of rac-naproxen starting from commercially available 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid. DOI: 10.1134/S107042802560130X
✓ The Pd-catalyzed hydroxycarbonylation of vinyl acetate in the presence of formic acid into 2-acetoxy propionic acid is reported. The proposed method is characterized by very mild reaction conditions (80°C, 3–6 bar CO pressure) and exceptionally high chemo- and regioselectivity to the target acid. DOI: 10.71267/mencom.7657
✓ Supported zinc-containing catalysts are considered as a viable alternative to the currently-deployed Cr-based (toxic) and Pt-based (costly) catalysts of alkane dehydrogenation, as reflected also in the increased number of reports related to the Zn-based catalysts in recent years. Here, we present a study of alumina-supported Zn-In and Zn-Mn propane dehydrogenation (PDH) catalysts prepared by the tailored methods. Specifically, the introduction of zinc relied on the chemical vapor deposition (CVD, using Zn vapor) onto alumina or alumina-supported indium or manganese materials, the latter two prepared by the impregnation of alumina with aqueous solutions of the respective metal nitrates followed by the calcination and hydrogen treatment. Alternatively, both zinc and indium were introduced by the co-impregnation of alumina with aqueous zinc and indium nitrates. The PDH tests revealed that the “dilution” of the active Zn2+ surface sites with In+ cations lead to a significant improvement in the catalytic performance, i.e., the introduction of In+ increased propene selectivity and attenuated the undesirable cracking and hydrogenolysis side reactions as well as decreased coke formation. In contrast, Mn2+ cations improved the catalytic properties of Zn2+ surface sites to a lesser extent than In+ cations. All prepared catalysts were characterized by DRIFT (diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform) spectroscopy of the adsorbed CO and H2 probe molecules. It was found that surface In+ and Mn2+ cations affect Zn2+ sites (electronic and geometric effect), which can be assessed from the position of the IR bands of zinc hydridespecies, formed due to the heterolytic hydrogen dissociation on the Zn2+ active sites. The effect of In and Mn dopants also was confirmed by the molecular DFT simulation. DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2024.114104