Laboratory of organic and metal-organic nitrogen-oxygen systems (№ 9)

ORCID: 0000-0003-4413-9453
Researcher ID: N-4877-2016
Scopus ID: 16065291000
h-index 23
- Reactivity of N-O bond-containing compounds
- Stereoselective synthesis of pharmaceutically relevant molecules
- Unstable organic intermediates
- Catalytic organic synthesis in a hydrogen atmosphere
- New heterocage structures
- Synthesis of fluorinated heterocycles
- New N-O-ligands for coordination chemistry and catalysis
- Spontaneous asymmetric induction
- Click-chemistry
✓ The concept of the alpha-effect of a heteroatom in a ligand has been proposed, which consists in stabilizing the high oxidation state +4 for d-metals (Mn, Fe, Ni, Co) in M-O-N type systems [Dalton Trans., 2025, 54, 9530]. The effect was discovered and studied in metals complexes with N-hydroxylated tri- and tetraazaadamantane ligands TRIAD and TAAD. The resulting cage-like complexes exhibit catalytic activity in the aerobic oxidation reactions of some organic compounds.
✓ Possible pathways for the involvement of nitrogen-oxygen compounds in the synthesis of biologically significant molecules prior to the emergence of life on early Earth have been analyzed [JACS Au, 2025, 5, 2420]. For the first time, an attempt has been made to develop a generalized picture of how the transition from inorganic N-O compounds to organic molecules, including amino acids, nucleosides, and their oligomers, could have occurred in a prebiotic environment.
✓ Enantioselective hydrogenation of E-β-enamido phosphonates to chiral β²-amino derivatives has been developed using an inexpensive and environmentally friendly nickel catalyst (13 examples with ee > 99%). [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 342]. This catalytic system also enables the hydrogenation of E/Z isomeric substrate mixtures with acceptable enantiomeric excess (up to 96% ee). It was demonstrated that the hydrogenation products can serve as starting materials for the synthesis of other chiral compounds, notably novel chiral β²-amino phosphine ligands. DFT calculations revealed that weak non-covalent interactions between the nickel catalyst and the substrate play a key role in achieving high enantioselectivity. The calculation results are also consistent with the fact that the hydrogenation of both E- and Z-isomers yields the same product enantiomer.
✓ A nitroso version of the Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley-Oppenauer reaction has been discovered, which constitutes an intramolecular 1,5-hydride transfer in δ-hydroxy gem-chloronitroso compounds. [Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 450]. DFT calculations revealed that the transformation proceeds via a concerted mechanism through a six-membered cyclic transition state. A three-step synthesis of annulated pyrrolidines using simple nitroalkenes and cycloalkenes or cyclodienes as starting materials has been developed using the discovered process.
✓ A new approach towards the ring opening of aryl-substituted donor-acceptor cyclopropanes (DAC) was proposed. [Org. Chem. Front., 2024, 11, 6483]. Based on it, the procedure for the ring opening of DAC with aliphatic nitro compou ds and other CH-acids in basic conditions was developed. Application of obtained products in organic synthesis was demonstrated, including preparation of gamma-aminobutyric acid analogues.
✓ An approach to circumvent the fundamental limitations of the aldol reaction associated with regio- and stereoselectivity has been proposed, utilizing the concept of umpolung of the reacting substrates. [J. Org. Chem., 2024, 89, 15590]]. For the first time, the synthesis of aldols has been successfully accomplished using reagents corresponding to the enolonium cation synthon (nitroalkenes) and the C-carbinol-anion synthon (sulfur ylides). Their condensation leads to the formation of nitrogen-oxygen heterocycles, isoxazoline N-oxides, which are readily cleaved to aldols under catalytic hydrogenation conditions. The developed method provides access to aldols with poorly accessible substitution patterns, which are of interest as precursors for pharmaceutical substances and natural molecules.
✓ A universal method for the regioselective assembly of N-protected pyrazoles has been developed via copper(I)-catalyzed alkynylation of aromatic α-halohydrazones with terminal alkynes, followed by cyclization of the transient α-alkynyl-substituted hydrazones. [Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 6999]. Heterocycles with a substitution pattern analogous to the obtained structures are found among pharmaceutically relevant compounds exhibiting anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antihypertensive, and antihyperglycemic activities.
✓ New annulation reactions involving aliphatic nitro compounds and vinyl sulfonium salts were described. [Org. Chem. Front., 2024, 11, 315]. Selective methods were proposed to control the direction of the reaction by changing a solvent (EtOAc, CF3CH2OH) and a base (DBU, NEt3), thus allowing selective preparation of nitrocyclopropanes or isoxazoline N-oxides. Bad on it, the procedure for the synthesis of polysubstituted cyclopropanes from nitrolakanes and styrenes was developed. The regioselectivity of the annulation of vinylsulfonium salts with nitroalkanes was assessed using quantum chemical calculations, showing the importance of hydrogen bond donor that coordinates with the nitronate fragment at the ring closure stage.
✓ The reaction of aryne precursors with cyclic nitronates was studied. Depending on the substrate structure, selective formation of various types of products is possible, including bicyclic nitroso acetals, 3-hydroxyphenyl-substituted 1,2-oxazines, and 3-substituted benzisoxazoles. [Org. Biomol. Chem., 2024, 22, 3615; J. Org. Chem., 2022, 87, 6838]. The transformation proceeds as a [3+2] cycloaddition followed by fragmentation of the nitroso acetal fragment. The resulting products are promising for medicinal chemistry and also serve as convenient precursors for pharmacologically important 1,4-amino alcohols and other compounds.
✓ A fundamentally new type of macrocyclic chelator has been developed — macrocyclic poly-N-hydroxyamines (so-called crown-hydroxylamines) [Nature Commun., 2023, 14, 7673]. These ligands form stable complexes containing a d-metal ion coordinated by several hydroxylamine fragments simultaneously. Crown-hydroxylamine complexes exhibit pH-dependent behavior, with their metal-binding efficiency increasing upon deprotonation of the N-OH groups. Due to their ability to activate molecular oxygen, crown-hydroxylamine complexes hold potential for application in biomimetic oxidation catalysts.
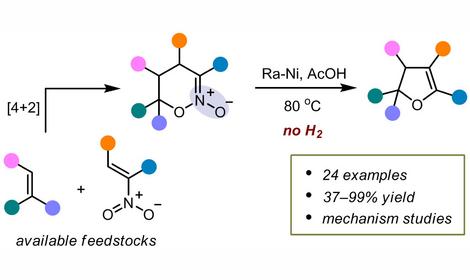
✓ A efficient synthesis of polysubstituted 2,3-dihydrofurans has been solved in two steps from readily available nitroalkenes and olefins. [Adv. Synth. Catal. 2023, 365, 2850]. The method is based on a catalytic reductive denitration of 1,2-oxazine N-oxides, leading to the contraction of a six-membered ring into a five-membered one. The process utilizes readily available and inexpensive Raney nickel, which acts as both a catalyst and a stoichiometric reagent, without the need for high-pressure equipment or explosive hydrogen gas.
✓ A generalized model for the origin of asymmetric induction in organocatalytic reactions and processes catalyzed by transition metal complexes with chiral ligands has been proposed [Catalysts 2022, 12, 214; Nature Chem. 2022, 14, 920]. Using the example of asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation, it was shown that hydrogen activation by metal atoms and asymmetric induction by ligands occur independently of each other, and the entire process can be considered a variant of cooperative organocatalysis. This conclusion expands the possibilities for the rational design of catalyst structures for asymmetric transformations.
✓ A diastereoselective approach to the synthesis of an important class of pharmacologically active piperidines has been developed via a previously unknown catalytic cyclization of readily available 1,5-dioximes [Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 2557]. The process enables the synthesis of analogs of known pharmaceutical drugs with novel substitution patterns. This work was recognized among the top scientific achievements of the N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry (ZIOC) in 2022.
✓ An novel cyclization of nitroalkyl-substituted malonic esters to isoxazolines under acylation conditions has been found [Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 2606]. Based on the discovered transformation, an approach for the assembly of polysubstituted isoxazolines (including those in asymmetric fashion) from readily available precursors was developed. Unlike many literature analogues, the isoxazoline ring closure is not redox-mediated, but rather a formal elimination of water from the substrate molecule.
✓ A method for the synthesis of 1,2-oxazines has been developed, based on a previously unknown reaction of cyclic nitronates with aryne precursors. [J. Org. Chem., 2022, 87, 6838]. The reaction involves [3+2]-cycloaddition followed by fragmentation of the nitrosoacetal moiety. 1,2-Oxazines represent a privileged scaffold in medicinal chemistry and also serve as convenient precursors to pharmacologically relevant 1,4-aminoalcohols and tetrahydrofurans.
✓ It has been demonstrated that the formaldehyde oxime trimer, tfoH3, forms transition metal complexes in an atypical high oxidation state +4. [Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 5523]. These stable complexes are formed from the corresponding Fe(III), Ni(II), and Mn(II) salts by air oxidation. The obtained complexes hold potential for interesting applications in catalysis (aerobic oxidation reactions) and analytical chemistry (spectrophotometric determination of transition metals). This work was recognized among the top scientific achievements of the N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry (ZIOC) in 2021.
✓ A 10-step asymmetric synthesis of Merck’s human neurokinin 1 (hNK1) receptor antagonist and three of its stereoisomers has been accomplished. [J. Org. Chem., 2020, 85, 11060]. Key steps of the developed approach include a [4+2]-cycloaddition, a site-selective C-H oxygenation utilizing a tandem acylation/[3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement, and the reductive contraction of a 1,2-oxazine ring into a pyrrolidine. The developed route is more efficient compared to the Merck synthesis, which comprises 13 steps and relies on reactions proceeding with low regio- and stereoselectivity. This work was recognized among the top scientific achievements of the N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry (ZIOC) in 2020 and highlighted in Synfacts.