Nazarov Laboratory of Fine Organic Synthesis (№ 11)

ORCID: 0000-0002-2280-3918
Researcher ID: P-7815-2017
h-index: 35
- Asymmetric organocatalysis;
- Organic synthesis under green chemistry conditions, particularly in liquefied or supercritical gases (carbon dioxide, lower freons, etc.) and water;
- Application of the developed methods for obtaining practically important compounds and materials, particularly energy-rich and medical ones.
✓ We have developed enantioselective cyanide- and nitro-free conjugate addition of allomaltol to chalcones or bis(arylidene)acetones in the presence of readily available C2-symmetric tertiary aminesquaramide organocatalyst to afford corresponding adducts in high yield with 84–99% ee. The procedure is readily scalable and the bifunctional catalyst can be recovered and reused in the catalytic reaction up to 8 times. The reaction products were converted without racemization to pharmacology relevant γ-functionalized carboxylic acid derivatives via oxidative cleavage of the γ-pyrone ring. Furthermore, unprecedented Ru(III)-catalyzed oxidative transformation of pyran-4-ones bearing the α,β-enone unit to chiral succinic acid derivatives via a one-pot oxidative fragmentation of both the γ-pyrone ring and activated C=C bond has been elaborated. The applicability of the prepared chiral compounds for facile asymmetric synthesis of GABAB receptor agonists, antidepressant drugs and monoaminooxidase (MAO) inhibitors has been demonstrated.
✓ The first practical enantiodivergent synthesis of bioactive indane-1-carboxylic acid derivatives is developed. A key step of the synthesis is highly enantioselective organocatalytic Michael addition of allomaltol, an available natural kojic acid derivative, to 1H-inden-1-ones. Subsequent oxidative fragmentation of the reaction products under the action of RuCl3/NaIO4 followed by chemoselective reduction of the resulting ketoacids with zinc amalgam afforded indane-1-carboxylic acids of high enantiomeric purity unavailable so far. The synthetic potential of the method was demonstrated by a gram-scale synthesis of (S)- and (R)-enantiomers of anticoagulant camonagrel.
✓ A powerful synthetic strategy for the asymmetric synthesis of enantiomerically enriched γ-functionalized α-amino acid derivatives based on the highly stereoselective prolinecatalyzed Mannich-type reaction of pre-prepared or in situ generated γ-pyrone-derived aldimines with carbonyl compounds and subsequent transformations of multifunctional reaction products has been developed. A significant positive nonlinear effect was detected for the key organocatalytic reaction. The developed strategy was applied for facile gram-scale preparation of (S)-γ-oxonorvaline, used for site-specific modification of proteins, and both enantiomers of amycolatolide A recently isolated from the lichen-derived actinomycete Amycolatopsis sp. YIM 130923.
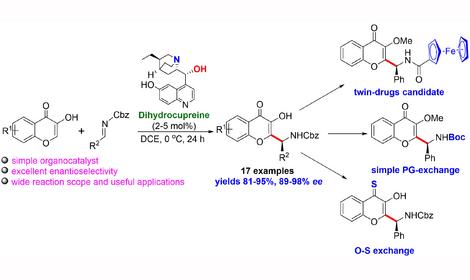
✓ A simple and efficient approach to chiral 2-substituted chromene-4-ones, bearing amino group linked to stereogenic center at the α-position with respect to the heterocycle is developed. Key feature of this approach is organocatalytic asymmetric addition of 3-hydroxychromen-4-one and its analogues to N-protected imines in the presence of commercially available natural alkaloid dihydrocuprein. Various benzaldimines bearing donor or acceptor groups in the aromatic ring, 1-naphthyl aldimine and nitrogen heterocycles imino derivatives proved to be suitable substrates for this reaction affording chiral adducts with enantioselectivity up to 98% ee. The chromene-4-one derived N-protected functionalized amines exhibit diverse reactivity that makes them perspective structural platform for the preparation of enantiomerically enriched bioactive compounds.
✓ We have developed most efficient nine-step total synthesis of (S)-Forphenicinol – active ingredient of immunomodulatory and anticancer remedy Forfenimexs, basing on available inexpensive substrates, including natural ones. The key stereogenic center was enantioselectively formed by hydroquinine-catalyzed asymmetric Mannich-type addition of kojic acid derived allomaltol to carefully designed N-Boc protected Schiff base. Subsequent oxidative fragmentation of the γ-pyrone fragment in α-position with respect to the amino group followed by deprotection afforded enantiomerically pure amino acid medication. The reactions are readily scalable and afford (S)-forphenicinol hydrochloride in 4-22-fold higher overall yield than those reported in the literature.
✓ An efficient enantioselective Mannich-type addition of vastly available allomaltol to N-tosylated aldimines catalyzed by dihydroquinine-based squaramide was elaborated. A concise gram-scale synthesis of non-proteinogenic (S)-aminoacids and their derivatives was achieved via the RuIII catalyzed oxidative fragmentation and subsequent transformations of the catalytic products.
✓ Biomass derived γ-pyrone-2-carbaldehydes were proposed as robust heterocyclic platform for carrying out organocatalytic asymmetric cross-aldol reactions with various aldehydes and ketones in high yield with excellent diastereoselectivity and enantioselectivity. Origins of efficient stereoinduction were revealed by quantum-chemical calculations of four possible transition states. The products were converted to synthetically useful chiral 2,4-dihydroxy carboxylic acid derivatives via protection/deprotection and RuIII-catalyzed oxidative fragmentation steps without racemization of stereogenic centers. The developed approach was applied for asymmetric synthesis of chiral pantolactones, valuable precursors of biologically active substances and natural products, and for synthesis of Dexpanthenol, a medication used for treating defects in the barrier function of skin.
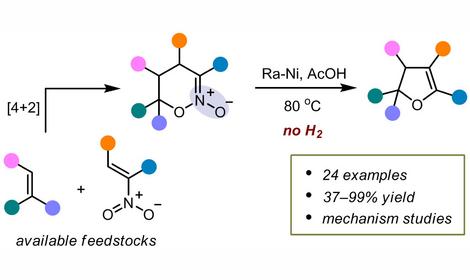
✓ 2-Nitroallylic carbonates were first applied as promising biselectrophilic C3 synthons for bifunctional squaramide catalyzed asymmetric domino reaction with kojic acid derivatives to afford so far inaccessible nitro compounds bearing two hydroxypyranone units. The reaction products undergo noncatalytic epimerization at the carbon atom next to the nitro group. Plausible mechanism of the epimerization based on reversible formation of intermediate aci-nitro compound is proposed. The double addition products were transformed to configurationally stable acetates and to chiral nitro glutarates, promising precursors to chiral amino glutaric acid derivatives.
✓ The evolution of modern catalytic methodologies for asymmetric organic synthesis, including transition metal and organocatalysis, is briefly considered. The results of the authors’ research group comprise the development of convenient, efficient, and reusable metal-free amine-containing catalysts (aminocatalysts) for manufacturing enantiomerically enriched organic compounds. The efficiency of the obtained catalysts is demonstrated for asymmetric aldol reactions, Michael reactions, and domino reactions, including green chemistry processes. The applicability of the developed catalysts and processes for the synthesis of natural product analogs and the most active enantiomers of clinically used drugs is demonstrated.
✓ The potential of carbon dioxide and 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane in their liquid and supercritical states as environmentally friendly (green) solvents for metal-free liquid-phase chemical transformations has been substantiated. This review summarizes data on N-, O-, and C-nitration carried out in these media. Particular attention is given to the application of liquid (liq-CO2) and supercritical carbon dioxide (sc-CO2) in condensation of carbonyl compounds with amines, including the one-pot tandem transformations of the resulting imines. The oxidative functionalization of cycloalkanes induced by near-UV light in the presence of nitrogen dioxide under sc-CO2 conditions is discussed. The effectiveness of sc-CO2 as a solvent in photooxidation of alcohols and sulfides with molecular oxygen in the presence of such metal-free photocatalysts as 2-fluoroanthraquinone and graphitic carbon nitride is demonstrated. Additionally, recent advances in asymmetric aldol reactions, conjugate additions, and cascade reactions catalyzed by chiral amines in liq-CO2 and sc-CO2 media are reviewed.
✓ Near-UV-light-induced oxidative conversion of cyclic and linear alcohols into corresponding carbonyl compounds was achieved in the supercritical CO2 medium under the action of molecular oxygen in the presence of 2-fluoroanthraquinone (1 mol%), a simple and available metal-free photocatalyst. A thorough examination of the impact of various process parameters on the reaction outcome allowed to identify a narrow density area at ~0.3 g/cm3 in the vicinity of the medium critical point and optimal reaction conditions (~45 °C, ~8.4 MPa) where up to 99% conversions and 65–93% yields of the oxidation products could be attained. Furthermore, compressed atmospheric air, a far cheaper and safer oxidizer than pure oxygen, can be applied to the reaction. Based on the experimental data, a plausible mechanism of the photocatalytic process has been proposed comprising photocatalyst excitation with near-UV light followed by the hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) as the key stages.
✓ The research focuses on the innovative use of graphite-like carbon nitride (gC3N4) catalysts along with supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) for the green synthesis of valuable organic compounds. Having explored different synthetic routes for gC3N4 and the obtained samples efficiency in the photocatalytic oxidation of benzyl alcohol with molecular oxygen in scCO2, we identified the most effective catalyst bearing ether linkers between layers of a graphite-like structure. This catalyst facilitates the production of benzaldehyde and benzoic acid derivatives, highlighting the potential for sustainable industrial applications. The study’s emphasis on a metal-free catalyst and a zero-waste process underlines its contribution to environmentally friendly chemical practices. The proposed approach offers a more sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional processes in small-scale chemical production.
✓ Despite the extensive application of graphitic carbon nitride (gC3N4) and nanosized titanium dioxide (TiO2) in photocatalysis, data on direct comparison of their catalytic activity under similar conditions remain scarce. This study compares gC3N4 and TiO2 for aerobic sulfide oxidation in supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2), a green solvent. Under visible light irradiation, gC3N4 demonstrated high selectivity for sulfoxides due to its strong reductive properties, while TiO2 showed faster reaction rates but lower selectivity, driven by its higher oxidative potential. The distinct mechanisms of photooxidation on these catalysts are discussed, highlighting the electron transfer from photoactivated gC3N4 to oxygen and the direct oxidation of sulfides on the TiO2 photoinduced holes as the rate-determining steps. The work explored a wide substrate range, including aromatic and aliphatic sulfides, under optimized conditions. Both catalysts were successfully applied to the synthesis of a wide range of sulfoxides, particularly the precursor of the pharmaceutical Modafinil, demonstrating their practical utility despite moderate yields. This study underscores the potential of gC3N4 and TiO2 for sustainable and selective sulfide oxidation in a scCO2 medium, paving the way forgreener methods in producing valuable sulfur-containing compounds.
✓ For the first time, condensations of amines with carbonyl compounds have been performed in supercritical carbon dioxide (sc-CO2). The reactions with aldehydes or active ketones proceed at moderate temperatures (35–55 °C) without use of external catalysts. The process is autocatalytic: it is accelerated by the carbonic acid generated in situ by interaction between the released water and the CO2 medium. The imine products were obtained in high yields in a crystalline form and did not require further purification. The one-pot transfer hydrogenation and [4+2] cycloaddition reactions performed in the CO2 medium have uncovered attractive prospects for facile green synthesis of more complex and valuable compounds from the generated in situ imine products.
✓ An efficient and eco-friendly synthesis of α-amino nitriles through a three-component Strecker reaction in a supercritical CO2 medium has been developed. The attractiveness of the method comprises the use of a nearly equimolar KCN amount with a gradual formation of the true cyanating agent (HCN) under the action of in situ produced carbonic acid. The overall process runs in a sealed autoclave which ensures the full consumption of HCN over α-amino nitrile formation and excludes the exposure of a chemist to toxic HCN vapours. Readily attainable and mild reaction conditions (90 bar, 35 °C) along with scalability and safety make the developed procedure prospective for sustainable industrial applications.
✓ The continuous need for energetic materials with increased performance and improved safety characteristics stimulates synthetic efforts as well as physical modification of existing compounds. Herein we report the fabrication of 1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazoctane (HMX)-based composites with common commercial polymers, polymethyl acrylate (PMA), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene rubber (ABS), ethyl cellulose (EC), polylactide (PLA), and polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG). To precipitate the polymer on the HMX particles, the supercritical CO2-based anti-solvent method was employed. Surface state studies with various modes of scanning probe microscopy show that the polymers at less than 3 wt% content do not form a continuous layer but precipitate as globular islands. Nevertheless, the coating effectively absorbs the mechanical stress, resulting in a much lower sensitivity to impact and a considerable improvement of the HMX friction sensitivity. Specifically, for HMX@3PMA composite the impact and friction sensitivities are 54 J and 240 N, as compared to 7 J and 150 N for neat HMX. Additionally, the beneficial improvement of flowability is observed for the fabricated composites, and evidenced by small-scale flow cup studies. Importantly, the suggested procedure affords the safe and easy-to-handle energetic material powder containing only 1–3 wt% of the polymer additive.
✓ Novel catalyst-free method for functionalization of unbranched alkanes via radical nitration with UV-activated nitrogen oxide (IV) in supercritical carbon dioxide medium has been developed. The method allows to transform these inactive substrates into corresponding nitrates and nitro compounds with outstanding yields (up to 65%), using available reagents (NO2, O2) under mild reaction conditions (35–50 °C), and exhibits lower hazards compared to conventional analogues. An improved selectivity towards the nitrates has been achieved by adding pure oxygen to the reaction. Based on changes in reaction rate and product composition, the plausible reaction mechanism for the UV-induced C–H functionalization of alkanes with nitrogen oxide (IV) and pure oxygen has been proposed.